Research and development
The Cooling of generators by using hollow conductors in the wind energy
Reduction of tower head masses by integral construction and use of lightweight materials
 The reduction of the tower head mass has always been an important topic, because it is responsible for a great part of the structure costs. Apart from the usual methods to reduce masses for the generator and the structure, we do research aimed at increasing the percentage of lightweight construction material in wind turbines. In contrast to most wind turbines which dominate the market, including both turbines with gearboxes and those with direct drive, we developed a way to increase the amount of lightweight construction material. In our designs, the generator and rotor hub are constructed as a single part. This construction method was partially used in the project NEW82.
The reduction of the tower head mass has always been an important topic, because it is responsible for a great part of the structure costs. Apart from the usual methods to reduce masses for the generator and the structure, we do research aimed at increasing the percentage of lightweight construction material in wind turbines. In contrast to most wind turbines which dominate the market, including both turbines with gearboxes and those with direct drive, we developed a way to increase the amount of lightweight construction material. In our designs, the generator and rotor hub are constructed as a single part. This construction method was partially used in the project NEW82. In our new research projects the usability of lightweight materials will be
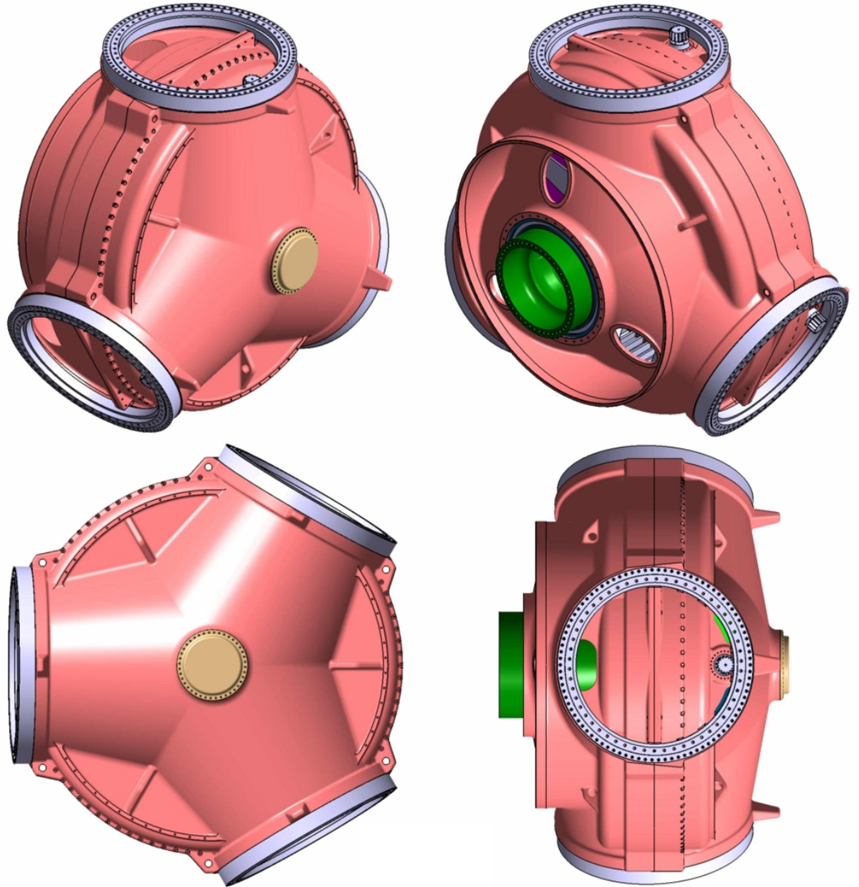
Specialized solutions for series production
Alternative solutions for blade pitch controls
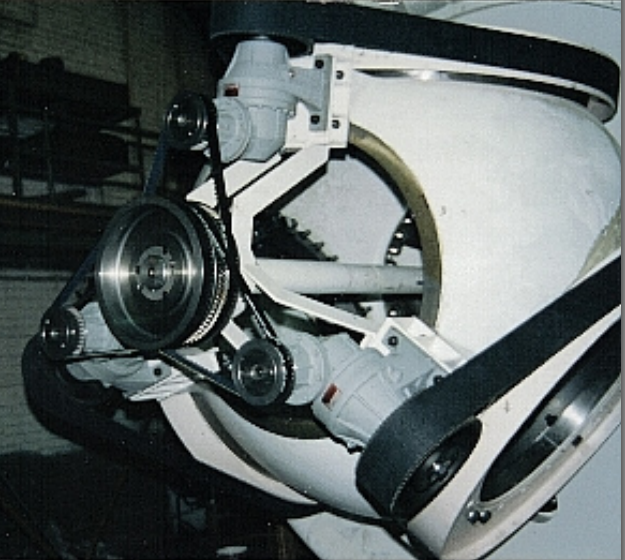 Pitch control is one of the most important systems of a modern wind turbine, and it requires considerable maintenance. Besides determining economic success by optimal positioning of the rotor blades in the wind direction, it is also responsible for power control, stopping and taking a resting position without risk. That is why INNOWIND took up this subject early and developed a pitch control system with a drive belt, wich is also used in VENSYS turbines.
Pitch control is one of the most important systems of a modern wind turbine, and it requires considerable maintenance. Besides determining economic success by optimal positioning of the rotor blades in the wind direction, it is also responsible for power control, stopping and taking a resting position without risk. That is why INNOWIND took up this subject early and developed a pitch control system with a drive belt, wich is also used in VENSYS turbines.Alternative solutions for the yaw control
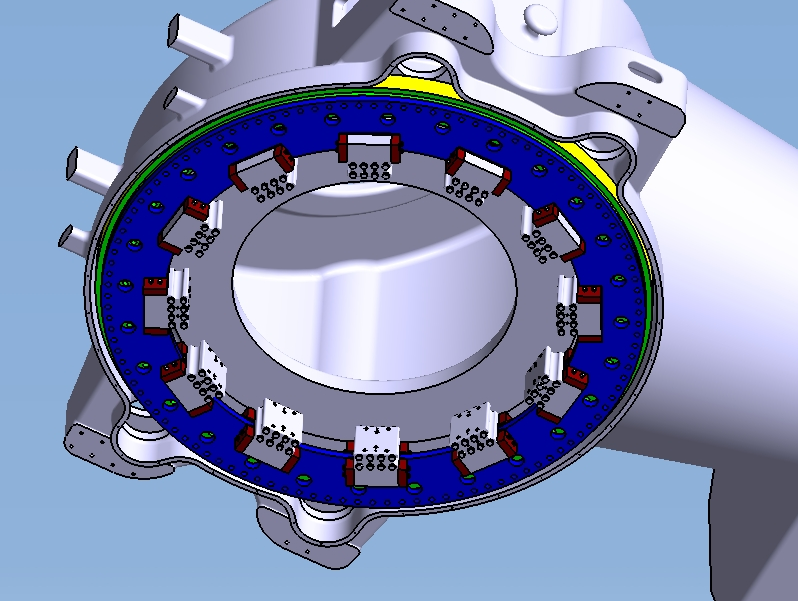 Regarding yaw control, systems with a high demand for maintenance are still the state of the art. For this reason, we do research and development works in the field of azimuth propulsion in order to find an alternative solution. This approach operates without a four-point-bearing with the help of a hydraulic fixation. We expect considerable improvements with regard to a lower maintenance and a simplified architectural system, which is economically more advantageous.
Regarding yaw control, systems with a high demand for maintenance are still the state of the art. For this reason, we do research and development works in the field of azimuth propulsion in order to find an alternative solution. This approach operates without a four-point-bearing with the help of a hydraulic fixation. We expect considerable improvements with regard to a lower maintenance and a simplified architectural system, which is economically more advantageous.
Automated assembly procedure for stator iron core
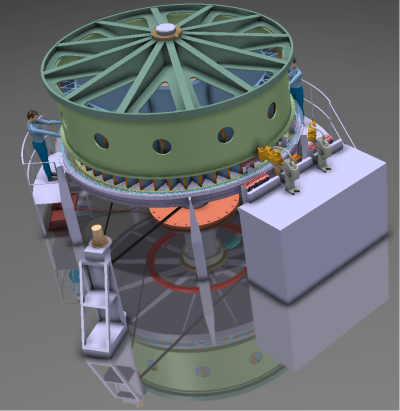 The iron core of an electrical machine consists of many layers of coated electrical sheets. These thin layers minimize the losses due to eddy currents. For handling reasons the sheets are segmented what leads to a high workload of more than 100 working hours to produce one iron core.
The iron core of an electrical machine consists of many layers of coated electrical sheets. These thin layers minimize the losses due to eddy currents. For handling reasons the sheets are segmented what leads to a high workload of more than 100 working hours to produce one iron core.
Concept for the electrical and mechanical testing of wind turbine
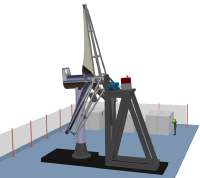 Wind turbines need to endure around 10e9 load cycles throughout their whole lifetime. Therefore a prediction of their fatigue strength is essential. Solely numerical simulations cannot fulfil this requirement and so physical fatigue testing is needed. Existing test rigs are very expensive since hydraulic actors are used to introduce high frequency aerodynamic loads.
Wind turbines need to endure around 10e9 load cycles throughout their whole lifetime. Therefore a prediction of their fatigue strength is essential. Solely numerical simulations cannot fulfil this requirement and so physical fatigue testing is needed. Existing test rigs are very expensive since hydraulic actors are used to introduce high frequency aerodynamic loads.
Feasibility study for a multi-rotor wind turbine
 Many manufacturers work on huge prototypes for bigger than current wind turbines. INNOWIND questions this continuous growth of single turbines. Based on theoretical principles it is shown that upscaling of turbines results in higher masses per MW and thus higher specific costs. Therefore we propose a multi turbine what is a wind plant with several rotors attached to one single tower. This approach seems to be economically more promising than further growth in turbine size.
Many manufacturers work on huge prototypes for bigger than current wind turbines. INNOWIND questions this continuous growth of single turbines. Based on theoretical principles it is shown that upscaling of turbines results in higher masses per MW and thus higher specific costs. Therefore we propose a multi turbine what is a wind plant with several rotors attached to one single tower. This approach seems to be economically more promising than further growth in turbine size.

